

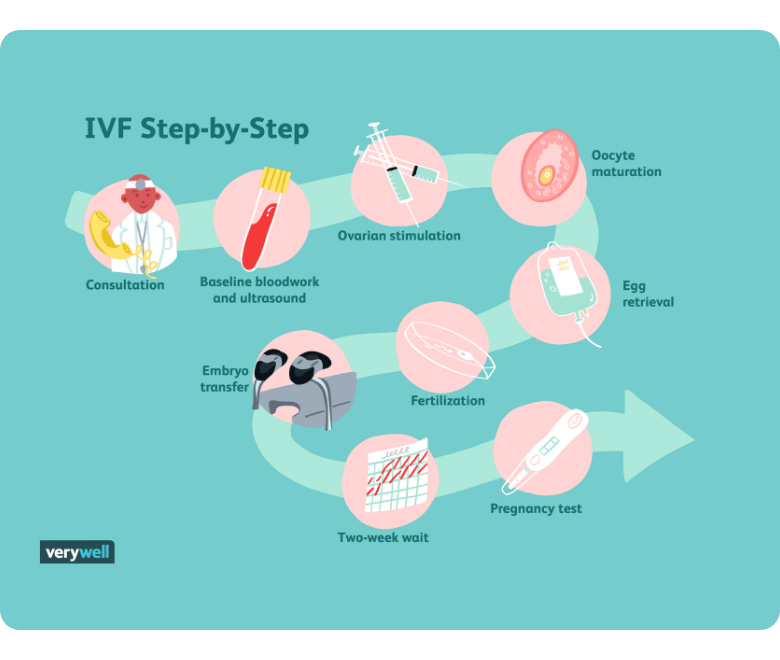
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a complicated sequence of methods used to assist with fertility or forestall genetic issues and help with the thought of a child.
During IVF, mature eggs are accumulated (retrieved) from ovaries and fertilized through sperm in a lab. Then the fertilized egg (embryo) or eggs (embryos) are transferred to a uterus. One full cycle of IVF takes about three weeks. Sometimes these steps are cut up into distinctive components and the procedure can take longer.
IVF is the most high-quality structure of assisted reproductive technology. The technique can be carried out the use of a couple’s personal eggs and sperm. Or IVF may additionally contain eggs, sperm, or embryos from an acknowledged or nameless donor. In some cases, a gestational provider — anybody who has an embryo implanted in the uterus — may be used.
Your probabilities of having a wholesome child the use of IVF rely on many factors, such as your age and the motive of infertility. In addition, IVF can be time-consuming, high priced and invasive. If greater than one embryo is transferred to the uterus, IVF can result in a being pregnant with extra than one fetus (multiple pregnancy).
Your health practitioner can assist you recognize how IVF works, the plausible dangers and whether this approach of treating infertility is proper for you.
(IVF) is a remedy for infertility or genetic problems. If IVF is carried out to deal with infertility, you and your companion would possibly be capable to strive less-invasive cure selections earlier than trying IVF, along with fertility tablets to amplify manufacturing of eggs or intrauterine insemination — a system in which sperm are positioned without delay in the uterus close to the time of ovulation.
Sometimes, IVF is supplied as a main cure for infertility in ladies over age forty IVF can additionally be accomplished if you have sure fitness conditions. For example, IVF may additionally be a choice if you or your associate has:
· Fallopian tube harm or blockage. Fallopian tube injury or blockage makes it challenging for an egg to be fertilized or for an embryo to tour to the uterus.
· Ovulation disorders. If ovulation is rare or absent, fewer eggs are accessible for fertilization.
· Endometriosis. Endometriosis happens when tissue comparable to the lining of the uterus implants and grows backyard of the uterus — regularly affecting the characteristic of the ovaries, uterus and fallopian tubes.
· Uterine fibroids. Fibroids are benign tumors in the uterus. They are frequent in female in their 30s and 40s. Fibroids can intervene with implantation of the fertilized egg.
· Previous tubal sterilization or removal. Tubal ligation is a kind of sterilization in which the fallopian tubes are reduce or blocked to completely forestall pregnancy. If you desire to conceive after tubal ligation, IVF can also be an choice to tubal ligation reversal surgery.
· Impaired sperm manufacturing or function. Below-average sperm concentration, susceptible motion of sperm (poor mobility), or abnormalities in sperm dimension and form can make it challenging for sperm to fertilize an egg. If semen abnormalities are found, a go to an infertility expert may be wanted to see if there are correctable troubles or underlying fitness concerns.
· Unexplained infertility. Unexplained infertility skill no purpose of infertility has been determined regardless of comparison for frequent causes.
· A genetic disorder. If you or your accomplice is at threat of passing on a genetic disease to your child, you may additionally be candidates for preimplantation genetic trying out — a manner that includes IVF. After the eggs are harvested and fertilized, they're screened for sure genetic problems, even though no longer all genetic troubles can be found. Embryos that do not incorporate recognized issues can be transferred to the uterus.
· Fertility maintenance for most cancers or different fitness conditions. If you are about to begin most cancers remedy — such as radiation or chemotherapy — that may want to damage your fertility, IVF for fertility maintenance may additionally be an option. Women can have eggs harvested from their ovaries and frozen in an unfertilized nation for later use. Or the eggs can be fertilized and frozen as embryos for future use.
· Women who do not have a useful uterus or for whom being pregnant poses a serious fitness threat may pick out IVF the usage of every other man or woman to lift the being pregnant (gestational carrier). In this case, the woman's eggs are fertilized with sperm, however the ensuing embryos are positioned in the gestational carrier's uterus.
Before beginning a cycle of IVF using your own eggs and sperm, you and your partner will likely need various screenings, including:
Ovarian reserve testing. To determine the quantity and quality of your eggs, your doctor might test the concentration of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), estradiol (estrogen) and anti-Mullerian hormone in your blood during the first few days of your menstrual cycle. Test results, often used together with an ultrasound of your ovaries, can help predict how your ovaries will respond to fertility medication.
Semen analysis. If not done as part of your initial fertility evaluation, your doctor will conduct a semen analysis shortly before the start of an IVF treatment cycle.
Infectious disease screening. You and your partner will both be screened for infectious diseases, including HIV. Practice (mock) embryo transfer. Your doctor might conduct a mock embryo transfer to determine the depth of your
uterine cavity and the technique most likely to successfully place the embryos into your uterus. Uterine exam. Your doctor will examine the inside lining of the uterus before you start IVF. This might involve a son hysterography — in which fluid is injected through the cervix into your uterus — and an ultrasound to create images of your uterine cavity. Or it might include a hysteroscopy — in which a thin, flexible, lighted telescope (hysteroscope) is inserted through your vagina and cervix into your uterus.
IVF can be presented into the following steps:
Before you start IVF treatment, your doctor may prescribe birth control pills or estrogen. This is used to stop the development of ovarian cysts and control the timing of your menstrual cycle. It allows your healthcare provider to control your treatment and maximize the number of mature eggs during the egg retrieval procedure. Some people are prescribed combination birth control pills (estrogen and progesterone), while others are given just estrogen.
During every herbal cycle in a wholesome individual of reproductive age, a crew of eggs starts off evolved to mature every month. Typically, solely one egg will become mature sufficient to ovulate. The closing immature eggs in that team disintegrate.
During your IVF cycle, you’ll take injectable hormone medicinal drugs to motivate the complete crew of that cycle’s eggs to mature concurrently and fully. This means, as an alternative of having simply one egg (like in a herbal cycle), you may additionally have many eggs. The type, dosage and frequency of medicines prescribed will be tailor-made to you as an man or woman primarily based on your clinical history, age, AMH (anti-Mullerian hormone) degree and your response to ovarian stimulation for the duration of previous IVF cycles. It consists of two steps:
· Monitoring
· Trigger shot.
Your doctor makes use of an ultrasound to information a skinny needle into every of your ovaries thru your vagina. The needle is linked to a suction system used to pull your eggs out of every follicle. Your eggs are positioned in a dish containing a distinct solution. The dish is then put in an incubator (controlled environment). Medication and slight sedation are used to limit pain all through this procedure. Egg retrieval is achieved 36 hours after your ultimate hormone injection, the “trigger shot.”
The afternoon after your egg retrieval procedure, the embryologist will strive to fertilize all mature eggs using intracytoplasmic sperm injection, or ICSI. This means that sperm will be injected into every mature egg. Immature eggs cannot have ICSI performed on them. The immature eggs will be positioned in a dish with sperm and nutrients. Immature eggs rarely finish their maturation procedure in the dish. If an immature egg does mature, the sperm in the dish can then attempt to fertilize the egg.
On average, 70% of mature eggs will fertilize. For example, if 10 mature eggs are retrieved, about seven will fertilize. If successful, the fertilized egg will become an embryo.
If there are an extraordinarily large number of eggs or you don’t choose all eggs fertilized, some eggs may be frozen before fertilization for future use.
Over the next five to six days, the development of your embryos will be carefully monitored.
Your embryo must overcome significant hurdles to become an embryo suitable for transfer to your uterus. On average, 50% of fertilized embryos progress to the blastocyst stage. This is the stage most suitable for transfer to your uterus.
For example, if seven eggs were fertilized, three or four of them might develop to the blastocyst stage. The remaining 50% typically fail to progress and are discarded.
All embryos suitable for transfer will be frozen on day five or six of fertilization to be used for future embryo transfers.
Embryo transfer
A sparkling embryo transfer means your embryo is inserted into your uterus between three and seven days after the egg retrieval procedure. This embryo hasn’t been frozen and is “fresh.”
A frozen embryo switch means that frozen embryos (from a previous IVF cycle or donor eggs) are thawed and inserted into your uterus. This is a extra common practice for logistical motives and because this method is extra likely to result in a stay birth. Frozen embryo transfers can occur years after egg retrieval and fertilization.
As part of the first step in a frozen embryo transfer, you’ll take oral, injectable, vaginal, or transdermal hormones to put together your uterus for accepting an embryo. Usually, this is 14 to 21 days of oral medication followed by using six
days of injections. Typically, you’ll have two or three appointments during this time to monitor the readiness of your uterus with ultrasound and to measure your hormone ranges with a blood test. When your uterus is ready, you’ll be scheduled for the embryo transfer procedure.
The process is comparable if you’re using fresh embryos, barring embryo transfer happens inside three to five days of being retrieved.
The embryo transfer is a easy procedure that doesn’t require anesthesia. It feels like a pelvic examination or Pap smear. A speculum is placed within the vagina, and a skinny catheter is inserted through the cervix into the uterus. A syringe attached to the different end of the catheter contains one or extra embryos. The embryos are injected it the uterus through the catheter. The procedure usually takes less than 10 minutes.
Pregnancy occurs when the embryo implants itself into the lining of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will use a blood test to determine if you’re pregnant approximately nine to 14 days after embryo transfer.
If donor eggs are being used, the same steps are taken. The egg donor will complete ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval. After fertilization takes place, the embryo is transferred to the person who intends to carry the pregnancy (either with or without various fertility medications).
There are many factors to take into consideration before starting IVF treatment. To get the best understanding of the IVF process and what to expect, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider.
During your IVF cycle, you’ll take injectable hormone medications to encourage the entire group of that cycle’s eggs to mature simultaneously and fully. Your healthcare provider will determine the type of drug, frequency, and dosages you need for your treatment. This is based on your age, medical history, hormone levels and your response to previous IVF cycles if applicable. You can expect to inject fertility medicine for around eight to 14 days.
Contact Us